“Co-processing is crucial for cement industries as it offers a more environmentally sound alternative to full energy recovery and material recycling” - NordCham Sustainability Committee statement
The NordCham Sustainability Committee aims for more collaboration across industries and to learn from each other and experts. Since April 2022, the Sustainability Committee has hosted eight meetings on varying sustainability topics with resource speakers and sharing of best practices, networking opportunities and partnerships, and collaboration with government units.
The Committee is intended for business partners of NordCham, but guests with matching experience and responsibility are usually also accepted. Meetings have around 30 attendees representing a good mix of large, medium, and small-sized companies. Previous attendees represented companies from BDO, IKEA, AstraZeneca, Converge, SN Aboitiz Power, Arla Foods, etc.
Interested guests are welcome to contact Executive Director, Jesper Svenningsen at js@nordcham.com.ph. The next Sustainability Committee meeting will be on 22 February 2023 from 3:30 – 6:00 PM at IWG Spaces, World Plaza, BGC. The topic of discussion is “Sustainable Transportation,” with speakers from DOTr, ABB, and Volvo. Registration can be accessed here.
The Nordic Chamber of Commerce of the Philippines Inc. welcomes 2023 by hosting its 8th Sustainability Committee Meeting on 25 January 2023 at IWG Spaces, World Plaza, BGC, with the topic Biofuel and Waste-to-Energy.
Attendees are representatives from BDO, Jollibee, AstraZeneca, Artelia Philippines, Multimind International, Nomura Research Institute, Nokia, SN Aboitiz Power, Isla Lipana & Co, Zenith Food Corporation, PTC Holdings Corp., Mantec International, BusinessWorld Publishing, Secura International, Caritas Health Shield, Secura International, and Reurasia Management Corporation.
The Committee Meeting focused on the companies’ initiative and practical steps of biofuel and waste-to-energy. The esteemed speakers were Mr. Darren Heppner, Founder of KeystonePartners and Keystone WorldBridge Holdings, Mr. Michael Simonsen, Sales Manager of Products and Upgrades at FLSmidth, and Atty. Angela Edralin-Valencia, Director of Ecoloop.
Mr. Heppner opened the Committee Meeting by presenting the Philippines’ increasing population growth that inevitably leads to a multiple of waste and garbage output. The use of plastics has been an enormous contributor to a linear model of “make, use, dispose” that caused large amounts of disposal in landfills and even polluting oceans and rivers.
To address this, Mr. Heppner discussed “mechanical” recycling – a process of recycling in ways of baking, melting, grinding, washing, separating, and compounding that ensures polymers remain intact. This is essential in reducing the process of recycling and saving manufacturing energy. He also introduced “advanced recycling,” a method of using chemicals and heat to change the molecular form into original components. This type of recycling is sustainable and innovative in recycling plastic as it converts the waste into new product/s that can be recycled multiple times.
Mr. Heppner also discussed “pyrolysis,” a thermal decomposition brought by a high temperature that alters the chemical composition. He raised an important point regarding the number of cars alongside tires needed in each vehicle. This became a pressing concern on where they would dump and what happened to used tires. Mr. Heppner quoted Bong Romero of Yokohama Philippines (2018), stating that the used tires end up in landfill and it’s the local government’s responsibility, tires usually get buried or burned. Currently, combustible components of tires are typically used as fuel in furnaces in cement manufacturing plants. Advanced countries adopt advanced recycling to granulate rubber and utilize it as a material for artificial turf.
Mr. Heppner proposed “advanced pyrolysis recycling” to manage and control waste; contribute to the economy and reduce waste output in the Philippines; and create new land, labor, and capital opportunities. He added the solutions matrix by implementing the collaboration among national builders, starting from Barangay-level to influence, to the Provincial or City/Town-level to lead, and to Top Executives to Champion.
Nevertheless, the Philippines has a long way to go regarding large-scale recycling. The current barrier realities of government regulations and cooperation, financial support from local investors, and competition from internal and external influencers are inevitable.

Afterward, Mr. Michael Simonsen from FLSmidth started his presentation by glancing at FLSmidth’s strategy for sustainable cement production. Currently, they are working on “Mission Zero” – FLS’ sustainability ambition enabling cement customers to move towards zero emissions, 100% fuel substitution, and zero waste. FLS has laid out its pathway to zero emissions by 2030, starting with efficiency improvements, fuel substitutions, clinker substitution, and finally, carbon capture.
Some highlighted points of Mr. Simonsen regarding the co-processing of waste in cement kilns:
“Co-processing refers to the use of wastes (referred to as “alternative fuels” for the purpose of energy and/or resource recovery with the result of reduced consumption of primary fuels and raw materials.”
Crucial for cement industries as it offers a more environmentally sound alternative to full energy recovery and material recycling.
It promotes the circular economy and offers society a valuable service by efficiently using municipal waste, hazardous and non-hazardous industrial waste, commercial waste, agricultural waste & residues, construction & demolition waste, and extractive (mining waste).
Co-processing has gained widespread acceptance in Europe, where some facilities have been able to replace up to 100% of conventional fossil fuels with AFs.
Benefits of alternative fuels: support waste management, reduce the use of fossil fuels, eliminate harmful substances, improve resource efficiency, and reduce GHG emissions.
Concept of waste co-processing: waste sourcing, waste preparation, material handling & storage, dosing, pyro processing, and quality control of cement.
Mr. Simonsen also reiterated the solutions and examples of co-processing
For finely shredded waste, including dosing and transport: low-cost solutions, maintaining minimal space requirements, suitable for receiving bulk materials from walking floor trucks and front loaders, and “plug & play solution.”
For coarse and bulky waste: high capacity solutions, customized versions & HOTDISC solutions, and combination solutions with pyro upgrades.
He further added the required waste quality for co-processing.
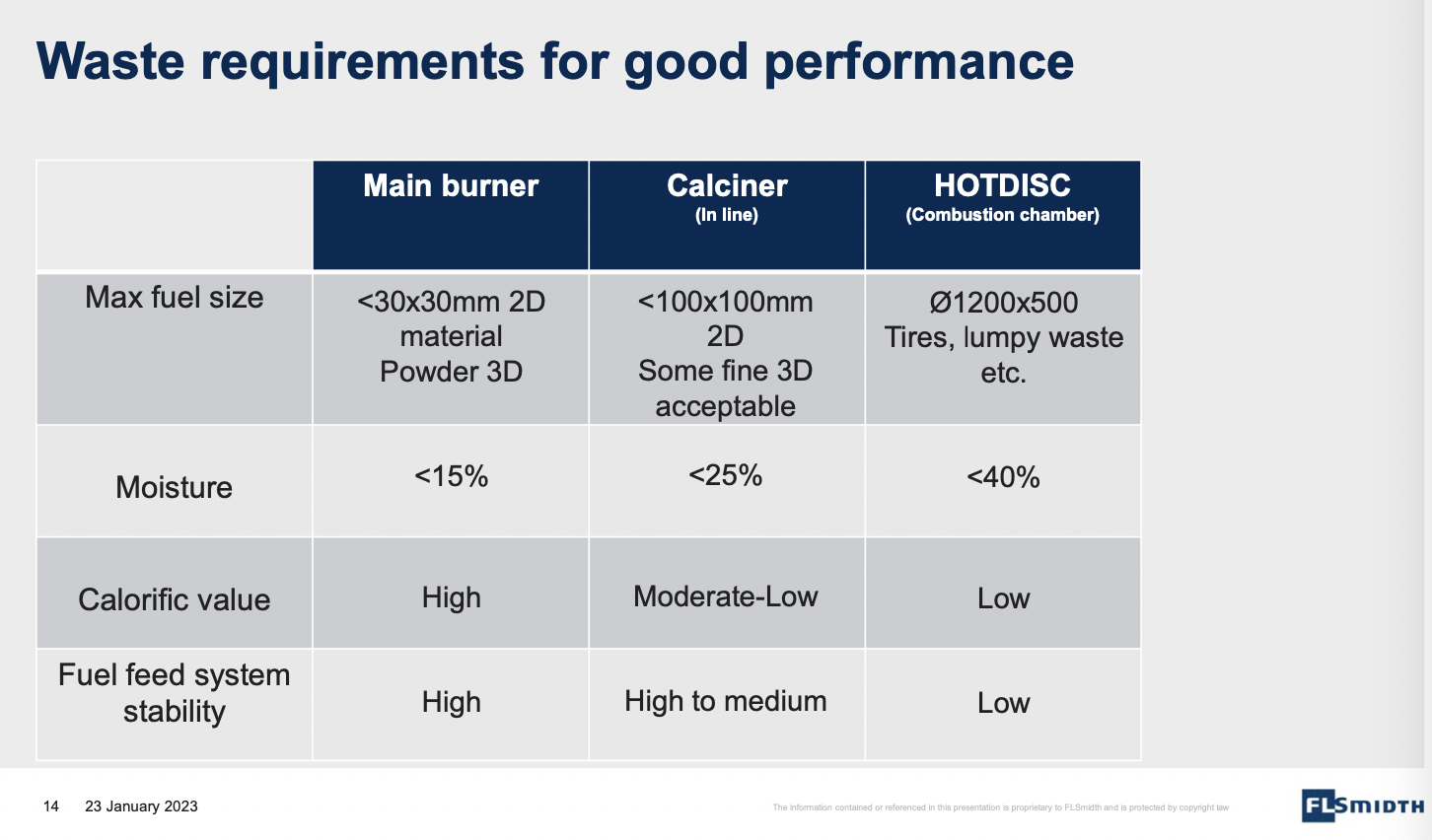
Indeed, fuel switching faces challenges such as sourcing of infrastructure & availability, environmental and commercial permits, waste preparation by spring, drying & shredding, waste handling in-plant storage, transportation and dosing, and quality impact on cement composition and ashes.

Finally, the last on the panel of speakers is Atty. Angela Edralin-Valencia. She started her presentation by introducing Republic Cement as a market leader with more than 65 years of experience in the cement manufacturing industry. They hold a strong presence in Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao.
Ecoloop is a resource group of Republic Cement Services. Its operations are embedded in sustainability – starting from a linear economy, evolving into a recycling economy, and now a circular economy. Co-processing of wastes in Kiln was part of their operation for more environmentally friendly and sustainable disposal of waste, promoting complete combustion, zero ashes, and less CO2 emission by replacing non-renewable materials.
Atty. Edralin-Valencia also reiterated the Pre-Consumer Waste and Post-Consumer Waste:
Zero-Waste to Landfill, starts from pre-consumer waste from manufacturers followed by waste collection to be co-processed at the cement plant.
Plastic Neutrality starts from manufacturer to plastic packaging, to consumer, to waste recovery (communities, LGUs, waste consolidators, landfills), and finally to co-processed at the cement plant.
Ecoloop has been doing co-processing for more than 20 years. They started biomass (2002). Later, they took a more complex stream of tires (2007) and industrial waste (2008). In 2011, they started RDF from MSW, while in 2018, Plastic Neutrality was their focus.
Atty. Edralin-Valencia also shared important points about the Extended Producer Responsibility Act of 2022.
EPR Law - large enterprises must recover up to 80% of their packaging footprint. Progress compliance is 20% by 2023 and 80% by 2028.
The penalty is twice the cost of collecting plastic footprint and disposing of it environmentally.
The obliged entities are the product producers, brand owners, manufacturers or importers. EPR Act covers large enterprises, SMEs are not covered, but they are encouraged.
The recovery programs to prevent waste leakage into the environment. First, redesign a product to ensure it's recyclable. Second, recovery programs in preventing harmful effects on the environment. Finally, redemption, buyback, or offsetting to recover plastics. Hereafter, diversion programs into value chains, back to value-adding products, and recycling or disposal more sustainably. Also, proper transportation of composting and recycling along with advocating waste clean-ups. Moreover, it encourages commercial or industrial-scale recycling, composting, thermal treatment, and other waste diversion or disposal facilities as vital players. Most importantly, partnerships with LGUs, communities, and informal sectors.
Compliance Timelines:
23 July 2022, EPR came into law
Six months from the effectivity of the EPR Law – entities are required to pass an EPR compliance plan that DENR needs to validate and approve
Third Party Compliance Audits for validation

After the three presentations, the participants engaged in a facilitated brainstorming session. Below are the highlights from the discussions:
Business opportunity for recycling tires
Importance of LGUs’ role in waste management even do companies and households do sorting
Financing instrument for green investment
Business care for waste-to-energy
Cement, pyrolysis facility challenges are logistics from facilities decentralized solutions
Property development sector, connect consumers back to producers
Public behavior change

The NordCham Sustainability Committee aims for more collaboration across industries and to learn from each other and experts. Since April 2022, the Sustainability Committee has hosted eight meetings on varying sustainability topics with resource speakers and sharing of best practices, networking opportunities and partnerships, and collaboration with government units.
NordCham Philippines looks forward to sustained collaboration and showcasing the sustainability initiatives of business partners while contributing to positive change by forging stronger relations with the government.

